PANEL OF JUDGES
专家委员会
“2025 Belonging Awards”A master level expert committee composed of the following senior experts provides professional guidance
MATERIALS AND RESOURCES
资料与资源
The 2024 “DEI Employer® Awards” Gala Dinner was successfully held in Dunhuang!
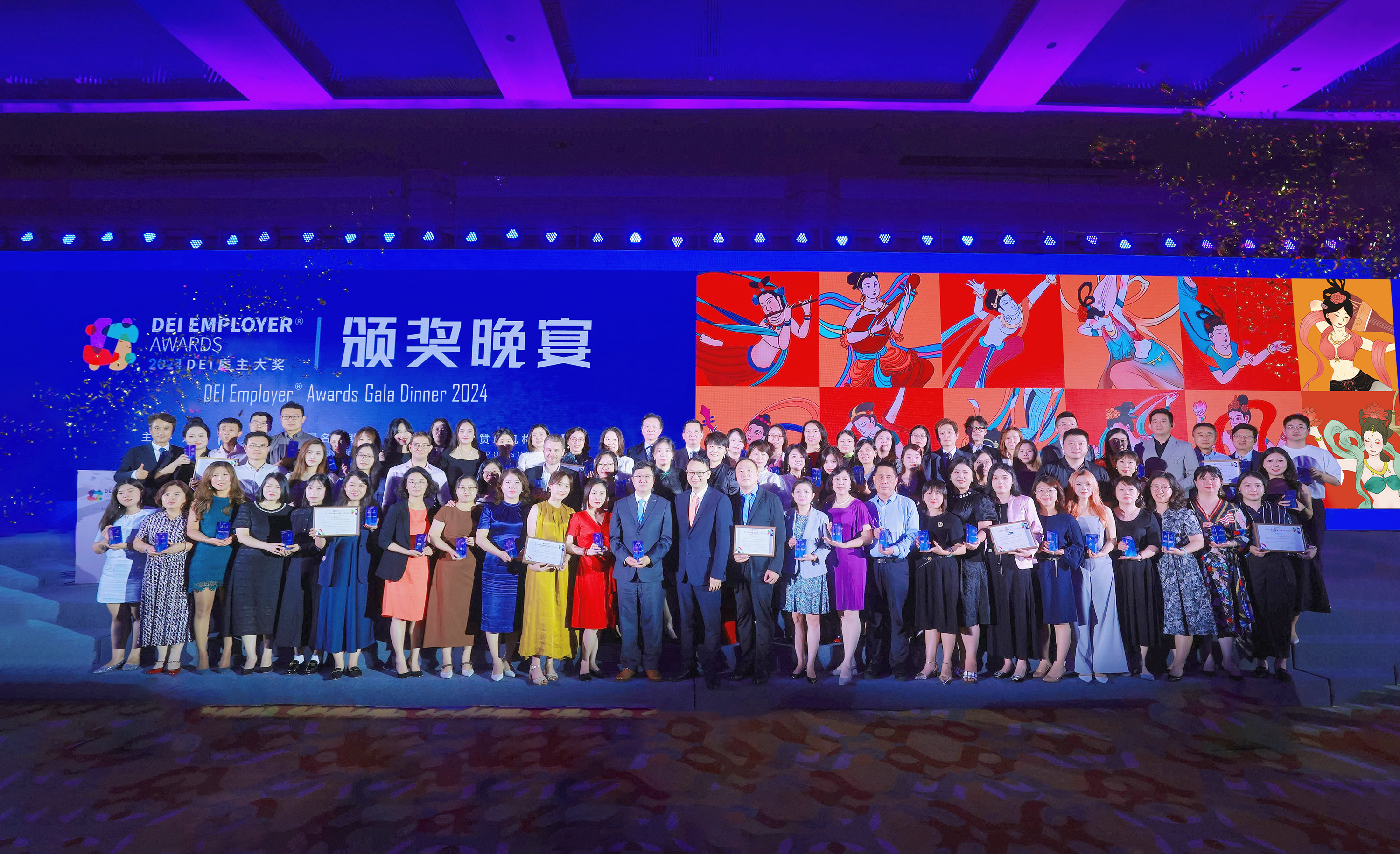

嘉宾演讲环节,由2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards评委、HRflag总经理-董炯炯先生介绍2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards
调研概览。

2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards评委、HRflag总经理-董炯炯先生带来主题分享
接下来,2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards评委、HRflag执行董事-唐秋勇博士围绕《DEI与中国》,带来精彩的主题分享。
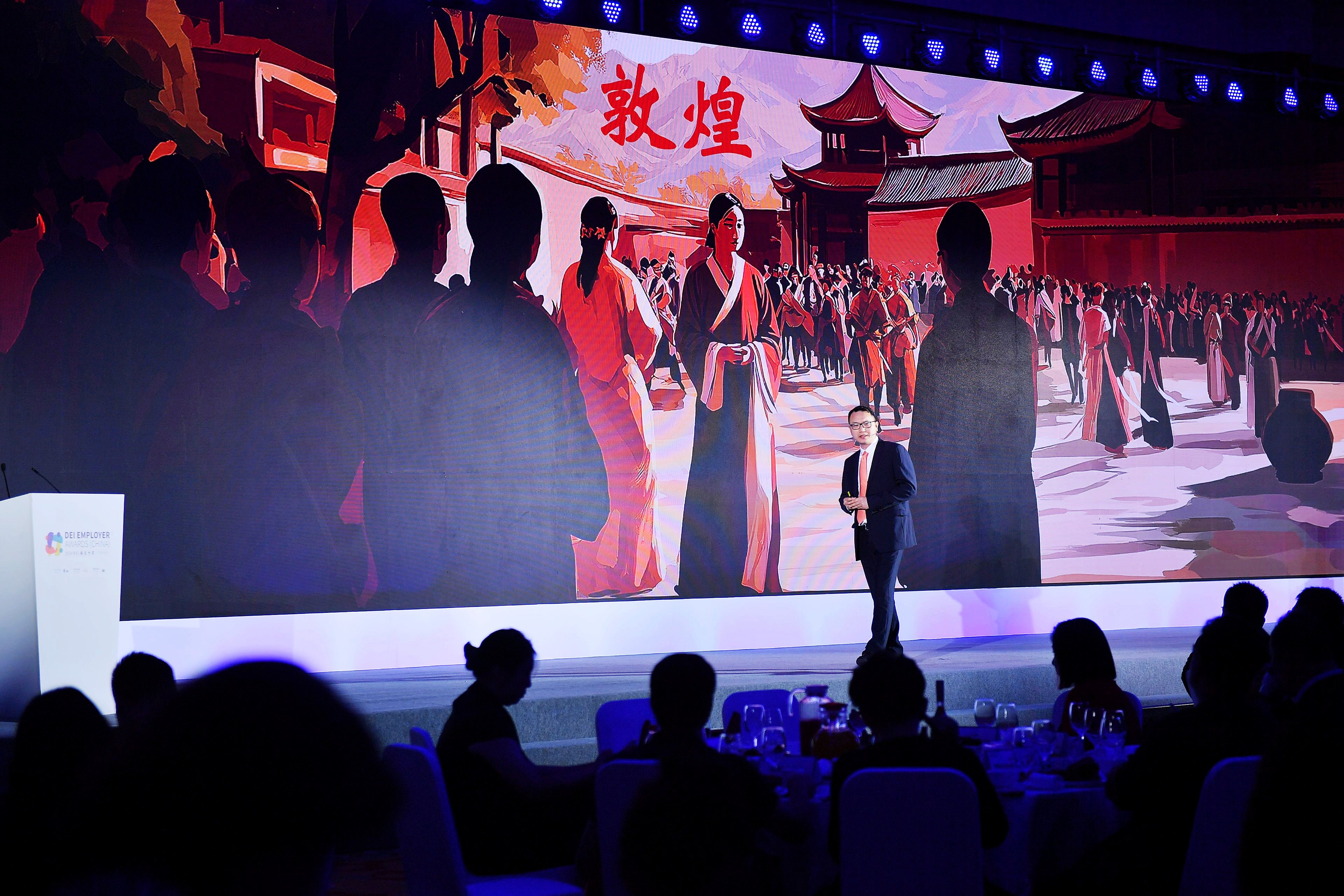



2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards评委、HRflag执行董事-唐秋勇博士带来主题分享
随后,2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards评委、雇主品牌研究所负责人-傅海洋女士发表主题演讲《引领多元未来,共创包容中国》。
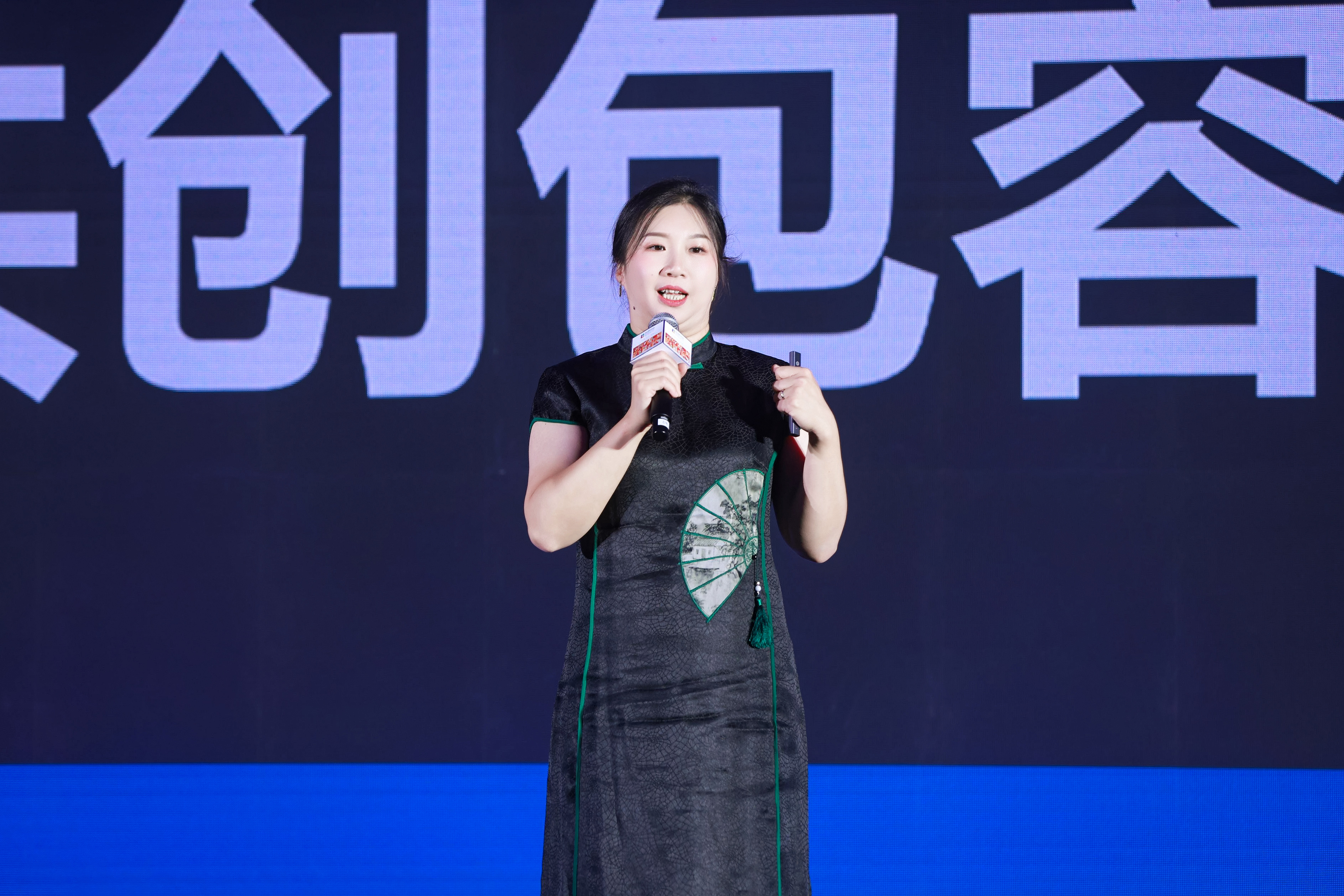


2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards评委、雇主品牌研究所负责人-傅海洋女士带来主题分享







点击查看“2024DEI雇主大奖(DEI Employer® Awards)”晚宴回顾

点击查看“2024DEI雇主大奖(DEI Employer® Awards)”晚宴回顾

点击查看2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards 奖项数据视频

点击查看2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards 概念视频

点击查看2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards 专家委员会介绍

点击查看“现代人力资源之父”戴夫·尤里奇(Dave Ulrich)贺辞视频

点击查看“雇主品牌之父”里查德·莫斯利(Richard Mosley)贺辞视频

点击查看2024“DEI雇主大奖” DEI Employer® Awards 颁奖视频

点击查看“DEI邂逅AI艺术共创”环节嘉宾作品

点击查看2024“DEI雇主大奖”DEI Employer® Awards获奖企业标识
2024 DEI Top 100 Employers List
TOP 100 DEI EMPLOYER® 2024

Employer Branding Institute has released the latest edition of "2024 TOP 100 DEl EMPLOYER®" ranking.
行业

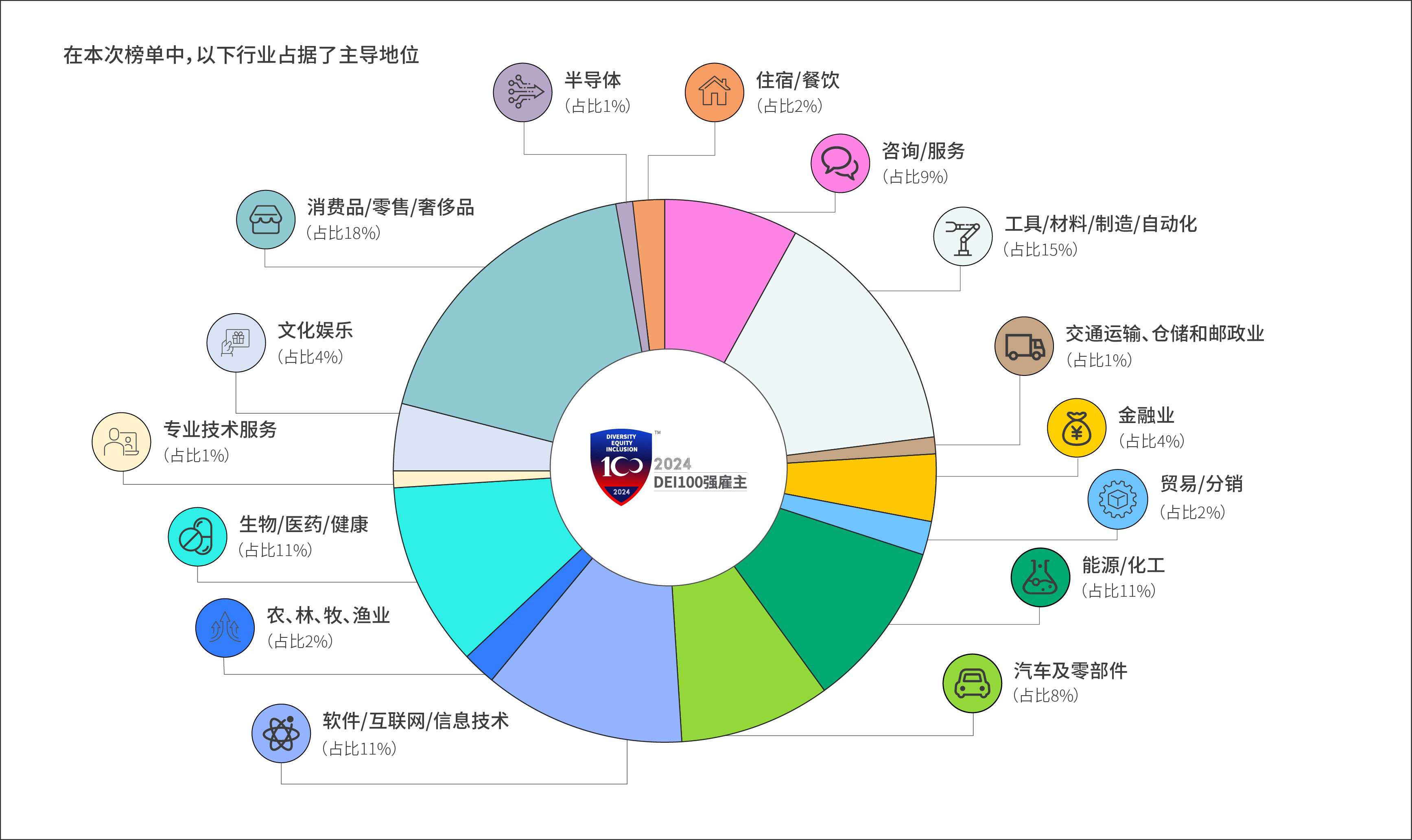
A comprehensive assessment was conducted based on the Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEl)
evaluation framework from the Employer Branding Institute (EBl), consisting of 10 major categories,
21 dimensions, and 103 evaluation indicators. The benchmarks and norms are based on the analysis of
3,871 samples from the Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) Analytics Platforms research database,
including data from 542 applicant companies for the "2024 DEI Employer® Award."
基于雇主品牌研究所(EBI)的DEI评估体系(10大类别、21个维度、103项评估指标)进行全面评估。基准和常模基于其多元、公平和包容分析平台(DEl Analytics Platforms)研究数据库的3,871份样本,含“2024DEI雇主大奖”542家申报企业数据。
DEI Employer ® 及其标识是雇主品牌研究所(EBI)的注册商标,其他标识为各自公司的商标或注册商标。
基于雇主品牌研究所(EBI)的DEI评估体系(10大类别、21个维度、103项评估指标)进行全面评估。基准和常模基于其多元、公平和包容分析平台(DEl Analytics Platforms)研究数据库的3,871份样本,含“2024DEI雇主大奖”542家申报企业数据。
DEI Employer ® 及其标识是雇主品牌研究所(EBI)的注册商标,其他标识为各自公司的商标或注册商标。
| 排名 RANK | 标识 LOGO |
|---|---|
|
1
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
3
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
6
|
|
|
7
|
|
|
8
|
|
|
9
|
|
|
10
|
|
|
11
|
|
|
12
|
|
|
13
|
|
|
14
|
|
|
15
|
|
|
16
|
|
|
17
|
|
|
18
|
|
|
19
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
21
|
|
|
22
|
|
|
23
|
|
|
24
|
|
|
25
|
|
|
26
|
|
|
27
|
|
|
28
|
|
|
29
|
|
|
30
|
|
|
31
|
|
|
32
|
|
|
33
|
|
|
34
|
|
|
35
|
|
|
36
|
|
|
37
|
|
|
38
|
|
|
39
|
|
|
40
|
|
|
41
|
|
|
42
|
|
|
43
|
|
|
44
|
|
|
45
|
|
|
46
|
|
|
47
|
|
|
48
|
|
|
49
|
|
|
50
|
|
| 排名 RANK | 标识 LOGO |
|---|---|
|
51
|
|
|
52
|
|
|
53
|
|
|
54
|
|
|
55
|
|
|
56
|
|
|
57
|
|
|
58
|
|
|
59
|
|
|
60
|
|
|
61
|
|
|
62
|
|
|
63
|
|
|
64
|
|
|
65
|
|
|
66
|
|
|
67
|
|
|
68
|
|
|
69
|
|
|
70
|
|
|
71
|
|
|
72
|
|
|
73
|
|
|
74
|
|
|
75
|
|
|
76
|
|
|
77
|
|
|
78
|
|
|
79
|
|
|
80
|
|
|
81
|
|
|
82
|
|
|
83
|
|
|
84
|
|
|
85
|
|
|
86
|
|
|
87
|
|
|
88
|
|
|
89
|
|
|
90
|
|
|
91
|
|
|
92
|
|
|
93
|
|
|
94
|
|
|
95
|
|
|
96
|
|
|
97
|
|
|
98
|
|
|
99
|
|
|
100
|
|